The Biophysics Core Facility: Overview
Core Facilities provide scientific resources, cutting-edge technologies and novel approaches to support DIR scientists. Availability of specialized expertise creates a robust environment for conducting a wide range of studies and accelerates the pace at which scientific discovery can take place.
The follow open access instruments are available in the core. First time users must complete training before gaining access to these instruments:
 |
Size (radius)Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)- DynaPro NanoStar IIIs for the precise analysis of thermally induced structural transitions in proteins, DNA, RNA, micellar complexes, and other biomolecular systems. Typical Applications:
|
 |
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) – ZetaView TWINTracks the Brownian motion of individual particles to measure their size, concentration, and zeta potential. Analyzes the properties of exosomes, micro vesicles, viruses, and nanoparticles. Typical Applications: |
 |
Structure/FoldingDifferential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) – Microcal VP-DSCUsed for the precise analysis of thermally induced structural transitions in proteins, DNA, RNA, micellar complexes, and other biomolecular systems. Typical Applications:
|
 |
Differential Scanning Fluorometry (nanoDSF) – Tycho NanometerUsed for the precise analysis of thermally induced structural transitions in proteins, DNA, RNA, micellar complexes, and other biomolecular systems. Typical Applications: |
 |
Circular Dichroism (CD) – Applied Photophysics Q100 with AutosamplerCD spectroscopy measures the difference in the sample absorption of the left and right circularly polarized light. For the randomly oriented samples, such as isotropic solutions, this difference will be observed for the chiral solute molecules. Typical Applications:
|
  |
SeparationFlow-Field Fractionation and Size Exclusion (FFF/SEC) OptilabMolecular separations and measurements of molecular mass, size, and shape of macromolecules in solution. Typical Applications:
|
 |
Molecular MassMulti-Angle Light Scattering (MALS)- Optilab and DawnMolecular separations and measurements of molecular mass, size, and shape of macromolecules in solution. Typical Applications:
|
 |
Analytical Ultracentrifugation (AUC) – Beckman Proteomelab XLIA gold-standard biomolecular analysis technique. A wide range of AUC-based methods are available for the analysis of interactions, oligomerization, composition, aggregation, membrane proteins, conformational changes, etc. Typical Applications: |
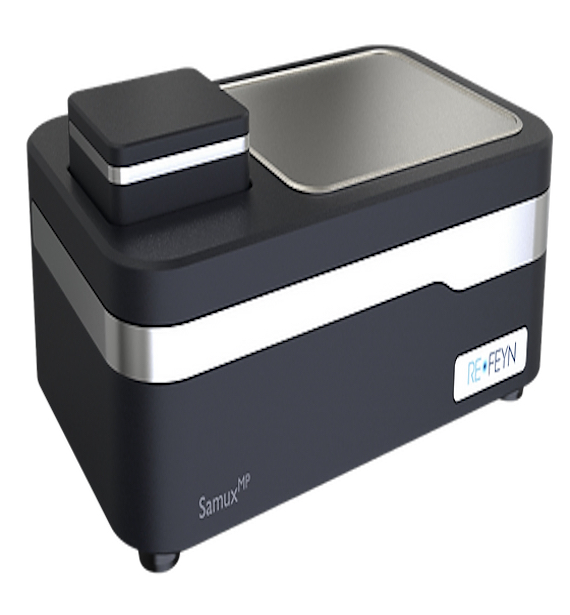 |
Mass Photometer (MP) – Refeyn OneMPNative state, label-free and immobilization free single-molecule mass analysis in solution. Typical Applications: |
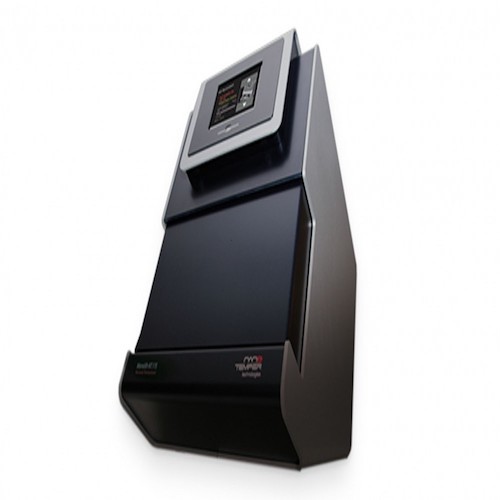 |
Binding AffinityMicroscale Thermophoresis (MST) – Nanotemper Monolith NT.115Challenging biomolecular interactions measured in solution using microliter-volume samples in a capillary format. A wide range of ligands and affinities can be analyzed in various buffer conditions, including cell lysates and plasma. Typical Applications: |
 |
Fluorescence – PTI/Horiba QuantaMasterA well established and universal method to study molecular interactions, conformation, stability, and to perform various biochemical assays. Typical Applications:
|
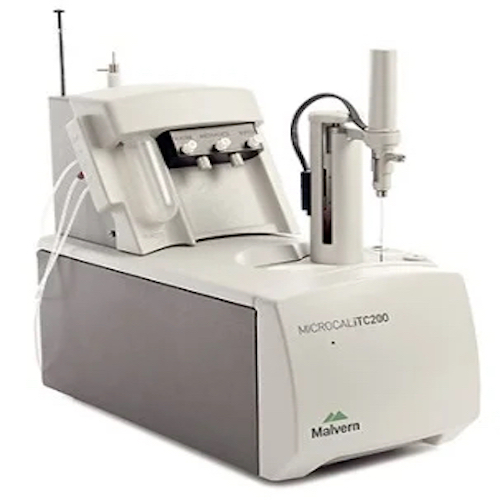 |
Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC) – iTC200Label-free and immobilization-free studies of biomolecular interactions in solution. Typical Applications:
|
 |
Microfluidic Diffusion Sizing (MDS) – Fluidity One-MMeasurements of interaction affinity, stoichiometry, ligand concentration, and molecular size in native conditions, including serum, plasma, and cell lysate. Typical Applications: |
 |
Binding KineticsBio-Layer Interferometry (BLI) – Octet RED96High-throughput, kinetic binding analysis using the 96-well plate format and eight parallel detectors. Ready-to-use biosensors for antibodies, as well as for biotinylated, His- and GST tagged proteins. Typical Applications: |


